SPECIFICITY VS SENSITIVITY OF A TEST
|
|
Specificity |
Sensitivity |
|
Definition |
It
is the percentage of people who
test negative for a specific disease among a group of people who
do not have the disease |
It is the percentage of people
who test positive for a specific disease among a group of people who have the
disease |
|
Easy to understand concept: |
The ability of a test to correctly identify people
without the disease. |
The ability of a
test to correctly identify patients with a disease. |
|
Other name |
true negative rate (TNR) |
true
positive rate (TPR) |
|
Interpretation |
The person does NOT
have the targeted disorder. |
The person has the
targeted disorder. |
|
Statistical Outcome |
True Negative |
True Positive |
|
The Rule |
Rule In (SpIn) SpPin:
A test with a high specificity value (Sp) that, when positive (P)
helps to rule in a disease (in). |
Rule Out (SnNout) A test with a high sensitivity value (Sn)
that, when negative (N), helps to rule out a disease (out) Rule In (Spin) |
|
Calculation: |
Specificity = Number of true negatives |
Sensitivity =
Number of true positives |
EXAMPLES
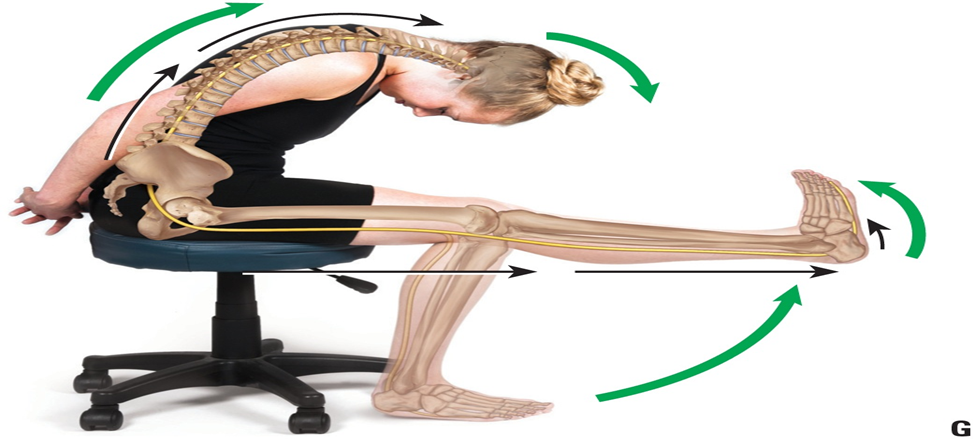
1. Slump Test:
- USED FOR: The Slump test is used to evaluate for lumbar nerve root impingement or irritation.
- SPECIFICITY: The slump test displayed high sensitivity (0.91)
- SENSITIVITY: moderate specificity (0.70)
2. SLR Test:
- USED FOR: The Straight Leg Raise (SLR) test is a commonly used test to identify impairment in disc pathology or nerve root irritation.
- SPECIFICITY: specificity is 0.89.
- SENSITIVITY: the sensitivity of the SLR test is 0.52.
3. Spurling
test:
- USED FOR: It is used during a musculoskeletal assessment of the cervical spine when looking for cervical nerve root compression causing cervical radiculopathy
- SENSITIVITY: The Spurling test had a sensitivity of 6/20 (30%)
- SPECIFICITY: specificity of 160/172 (93%).
4. Anterior drawer
test (knee joint):
- USED FOR: The anterior drawer test is a physical examination doctors use to test the stability of the knee's anterior cruciate ligament (ACL).
- SPECIFICITY: Its specificity is 91.43%
- SENSITIVITY: Its sensitivity is 93.33%
5. Anterior
Drawer Test (shoulder):
- USED FOR: The anterior drawer test (when pain does not prevent it from being performed) is helpful for diagnosing traumatic anterior instability)
- SPECIFICITY: The specificity of this test has been reported as 98.9%
- SENSITIVITY: low sensitivity of 52.8%
6. Crank test:
- USED FOR: This test also called labral crank test or compression rotation test is used to identify glenoid labral tears and assess an unstable superior labral anterior posterior (SLAP) lesions.
- SPECIFICITY: 56% specific
- SENSITIVITY: 46% sensitive
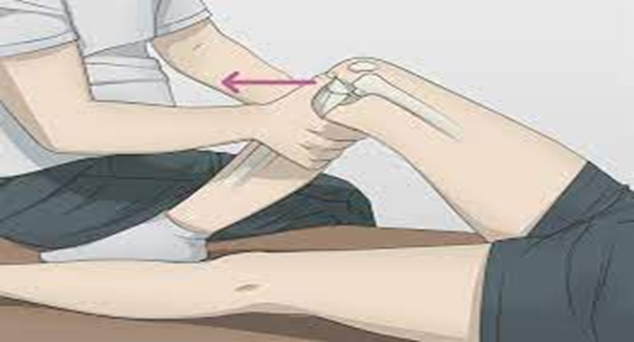
7. Tinel Sign:
- USED FOR: It's commonly used to diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome. the test can also be used to test for other nerve conditions, such as cubital tunnel syndrome, tarsal tunnel syndrome, or radial nerve injuries.
- SPECIFICITY: 93%
- SENSITIVITY: 62%
8. FABER TEST:
- USED FOR: The FABER test is used to identify the presence of hip pathology by attempting to reproduce pain in the hip, lumbar spine or sacroiliac region.
- SPECIFICITY: specificity is 66.7%.
- SENSITIVITY: Sensitivity is 50%.
9. Load and
shift test:
- USED FOR:The Load and Shift Test can be used to assess anterior as well as posterior shoulder instability.
- SPECIFICITY: 92.7% to 89.9%.
- SENSITIVITY: Gerber & Ganz report this test to be 100% sensitive
10. Talar tilt test:
- USED FOR: To test for injury to the lateral ligaments of the ankle.
- SPECIFICITY: Its specificity ranges from 68% and 88%
- SENSITIVITY: Sensitivity of the inversion talar tilt is reported to be 50% to 52%
THE END








Vast information in a nutshell. Welldone
ReplyDeleteGood information 👍 keep up the work doc.
ReplyDeletegood information
ReplyDelete