Introduction:
The radial nerve is a nerve that arises from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus and supplies the posterior side of the upper limb. Its nerve root is from C5 to C8 and T1.Wrist drop is a medical condition in which the entrapment or compression of RADIAL NERVE leads to decreased or blocked impulses to the extensor muscles of the arm, forearm and hand namely, It supplies the under mentioned muscles.
- Triceps Brachii (medial and lateral head)
- Brachioradialis
- Supinator muscle
- Anconeus
- Extensor carpi radialis longus
- Extensor carpi radialis brevis
- Extensor carpi ulnaris
- Extensor digitorum
- Extensor pollicis longus
- Extensor pollicis Brevis
- Extensor indices
- Extensor digiti minimi
- Abductor pollicis longus
MECHANISM OF INJURY IN WRIST DROP:
Radial nerve can be compressed or entrapped in FOUR major locations in the upper extremity that may lead to wrist drop. Even mild neuropraxia can cause severe effects and takes about 2-3 months healing time.- Triangular Interval entrapment(also called lower triangular space and triceps hiatus):
The radial nerve compresses in the triangular interval in some conditions like
Saturday night palsy: The term is typically used when an individual falls asleep with his/her arm handing over the back of the chair, this causes compression of the radial nerve in the triangular interval.
Crutch palsy: This term is typically used when radial nerve gets compressed by use of poorly fitted crutches in the axilla.
Honey moon palsy: The term is typically used when a loved or near one sleeps on the arm of a person thus compressing radial nerve in arm or in short triangular interval.
When the Radial nerve entraps in the triangular interval, It causes loss of motor and sensory functions along the route of the radial nerve and effects the muscles of the elbow and the wrist and digits and thumb, which are described above, thus causing wrist drop.
- Fracture of distal humerus shaft:

Wrist drop occurs when the humerus fractures distally along the spiral grove. This causes compression or tearing of the radial nerve thus causing sensory and motor loss along its route effecting muscles of the elbow, wrist and digits and thumb, described in introduction and causing wrist drop.
- Arcade of frohse or radial tunnel entrapment:
- Wearing too tight watches or any other piece of jewelry in hand:
SIGN AND SYMPTOMS:
- Pain in the wrist and hand (extensors)
- Tingling sensation in the wrist and hand (dorsal surface)
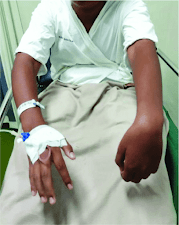
- Inability to extend wrist and fingers.
- Muscle atrophy of the extensors of the wrist and fingers (triceps, brachioradialis and supinator may also be involved as in crutch palsy.
TREATMENT THROUGH PHYSICAL THERAPY:
- Use of Braces and splints in order to support the wrist and hand
- Avoid repetitive movements of the wrist especially those involving extension and radial deviation (REST)
- Stretching Radial nerve in order to help in release from the point it is entrapped or compressed.
- Use of NSAIDS for pain relief.
- Use of EMG to send impulses to the muscles to prevent atrophy and faster recovery.
- Some physiotherapy exercises,
- active or active assisted ROM exercises of fingers, wrist, and elbow (Finger flexion, Finger extension,Finger abduction,Finger adduction, Wrist flexion, Wrist extension, Ulnar and radial deviation, elbow flexion, elbow extension, supination and pronation)
- Strengthening exercises of the muscles supplied by radial nerve.
- Stretching of supinator muscle (if it is the cause of radial nerve compression.)








Mashallah doctor sahab. 🤙
ReplyDeleteImpressive
ReplyDeleteExcellent
ReplyDelete