BONES AND IT'S TYPES ACCORDING TO DIFFERENT SHAPES:
INTRODUCTION:
Bones are rigid body tissue consisting of cells embedded in an abundant hard intercellular material.
It is composed of a number of constituents described bellow
TYPES OF BONES ACCORDING TO DIFFERENT SHAPES:
There are five types of bones when classified according to their shapes, namely
- Short bones:
- They are cube shaped (almost equal sides)
- short bones provide stability and some movement.
- Example:
- carpals ( scaphoid, lunate, triquetral, hamate, pisiform, capitate, trapezoid, and trapezium )
- Tarsals (calcaneus, talus, navicular, cuboid, lateral cuneiform, intermediate cuneiform, and medial cuneiform)
- Long bones:
- These are longer than they are wider, contain a wide shaft (diaphesis) and two extremities (epiphesis).
- Long bones function to support the weight of the body and facilitate movement
- Example:
- Long bones form the extremities, both upper and lower limbs.
- upper limb (humerus, radius, ulna, metacarpals, and phalanges)
- lower limb (the tibia, fibula, femur, metatarsals, and phalanges)

- Flat bones:
- Flat bones are thin, flattened, and usually curved.
- They usually function in protecting the vital organs of the body including heart, brain and pelvic organs.
- Example:
- skull (occipital, parietal, frontal, nasal, lacrimal, and vomer)
- thoracic cage (sternum and ribs)
- pelvis (ilium, ischium, and pubis)

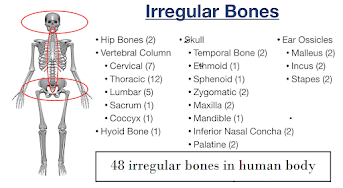
- Irregular bones:
- these bones are of complex shape.
- They are involved in supporting and protecting the internal organs of the body.
- Example:
- Vertebral column (vertebra, sacrum, coccyx)
- Skull (temporal,
sphenoid , ethmoid, zygomatic, maxilla, mandible, palatine, inferior nasal concha, and hyoid)
- Sesamoid bones (pea shaped):
- these bones are embedded in joint capsule or tendons and do not have any bony attachments.
- Sesamoid bones function to protect tendons from stress and wear.
- Example:
- Patella (knee cap)
- beneath the big toe joint
- pisiform bone in wrist




wow.
ReplyDelete