Knee Joint bones? Knee joint ligaments? Knee joint pain causes? Knee joint pain treatment? Knee joint physical therapy?
Knee Joint
INTRODUCTION:
Bony anatomy:
Knee joint is a uniaxial
synovial joint hinge joint. It is formed by two articulations
1.
The articulation
tibia and femur bone forming tibio-femoral joint
2.
The articulation
between patella and patellar grove on femur forming patella-femoral joint.
Ligaments:
There are 4 major
ligaments in knee joint, namely
- Medial collateral ligament (MCL) or tibial collateral ligament: It is present on the medial (inner) side of the knee, connects the femur with tibia. It supports the medial side of the knee.
- Lateral collateral ligament (LCL) or fibular collateral ligament: It is present on the lateral (outer) side of the knee, connects the femur to the fibula. It supports the lateral side of the knee.
- Anterior cruciate ligaments (ACL): It is located at the front of the knee. It plays a role in limiting anterior translation of femur over tibia, resist tibial rotation, provides valgus-varus stability when knee is fully extended, and to a lesser extent, it controls extension and hyperextension along with PCL.
- Posterior cruciate ligaments (PCL): It is located at the back of the ACL, at posterior knee joint. t plays a role in limiting posterior translation of femur over tibia, prevent excessive rotation of the knee, controls extension and hyper-extension of the knee.
COMMON CAUSES OF KNEE PAIN:
1.
Knee pain caused
by arthritis:
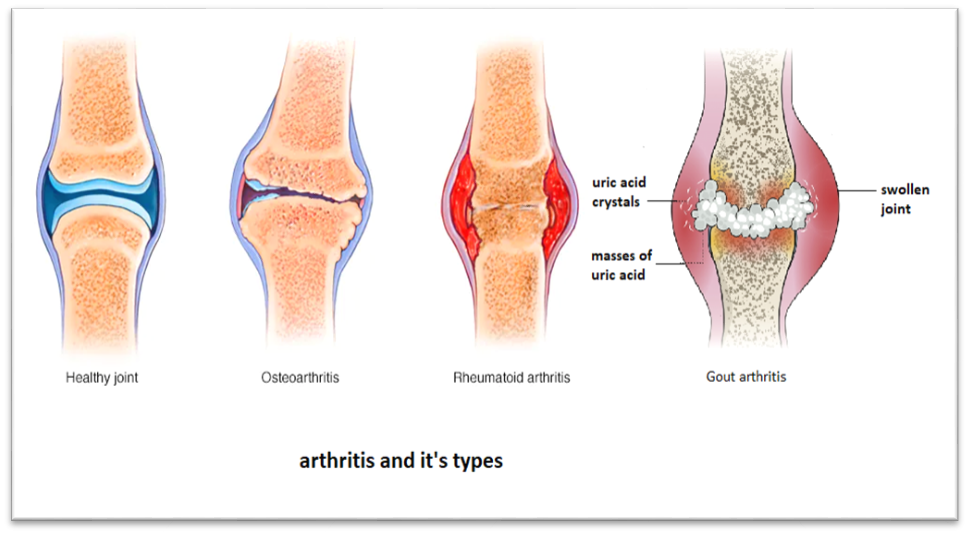
· Arthritis
is derived from two words, “Arthro” means joint and “it is” means inflammation,
so arthritis means inflammation or swelling of joints.
· There are three types of arthritis:
Osteoarthritis: It is a degenerative joint disease, in which the tissues in the joint break down over time.
Rheumatoid arthritis: It is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects a wide variety of systems of the body, including the joints, skin, eyes, lungs, heart, and blood vessels.
Gout arthritis: It is a painful form of inflammatory arthritis that usually affects the big toe, but can develop in any joint, including one or both of the knees. It is caused due to excessive accumulation of uric acid in blood.
· Arthritis
is caused by a number of factors including, wear and tear due to overuse (this
is also called osteoarthritis), age, obesity, auto-immune disease (in case of
rheumatoid arthritis), muscle weakness etc.
2.
Knee pain caused
by Baker’s cyst:
· Baker's
cysts, also known as popliteal cysts, it is a fluid-filled growth behind the
knee. It causes a bulge and a feeling of tightness.
· Baker's
cysts typically result from a problem inside the knee joint, such as
osteoarthritis/ arthritis or a meniscus tear
· In
response to this inflammation, the knee produces excess synovial fluid, which
travels behind the knee and accumulates in the popliteal bursa. The bursa then
swells and bulges, forming a Baker's cyst.
3.
Knee Pain caused
by cancer (osteosarcoma):
· It
is usually due to a primary tumor of the osseous structures or soft tissues of
the knee joint.
· Osteosarcoma
is an aggressive bone cancer. This type of cancer occurs when a bone-forming
cell starts growing out of control, making a malignant (cancerous) tumor in the
bone. Cancers that start elsewhere in the body and then metastasize (spread) to
bone are much more common than tumors that actually start in bone.
· It
is common in individuals ranging from 10-30 years (teenage growth spurts),
Being tall for a specific age, Previous treatment with radiation for another
cancer, especially at a young age or with high doses of radiation, Presence of
certain benign (noncancerous) bone diseases etc.
4.
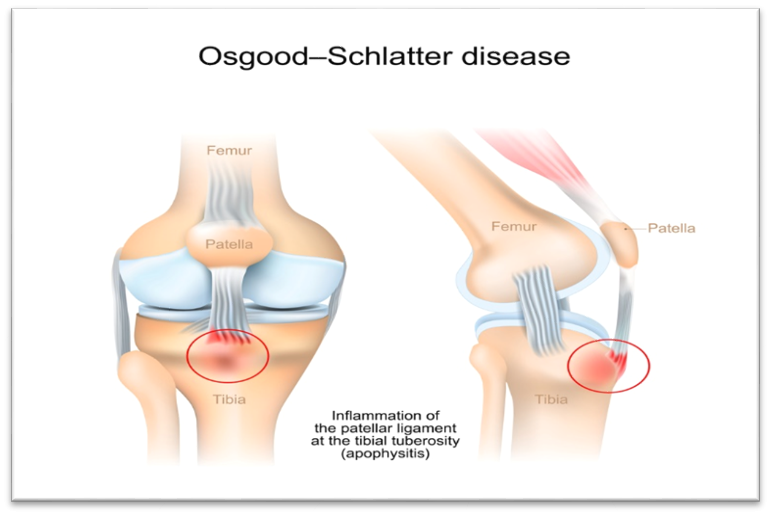
Knee pain caused
by Osgood Schlatter disease:
·
Osgood-Schlatter
disease is a condition that causes pain and swelling below the knee joint, where
the patellar tendon attaches to the top of the shinbone (tibia), a spot called
the tibial tuberosity,
·
Children and
adolescents get Osgood-Schlatter disease when they play sports that put
repeated stress on the patellar tendon, it can lead to tenderness at the point
where the patellar tendon attaches to the top of the tibia.
5.
Knee pain caused
by Infection:
·
A common example
of knee infection is septic arthritis.
·
Septic arthritis
is a painful infection in a joint that can come from germs that travel through
your bloodstream from another part of your body. Septic arthritis can also
occur when a penetrating injury, such as an animal bite or trauma, delivers
germs directly into the joint.
6.
Iliotibial band
syndrome:
·
IT band syndrome
is a common overuse injury, causing pain at the outside of the knee.
·
It occurs when the
iliotibial band gets irritated or swollen from rubbing against your hip or knee
bones.
SYMPTOMS OF KNEE INJURY:
Common symptoms faced by
patients suffering from knee injury include:
- Knee pain, from daily activities like walking, bending, standing and lifting
- Selling of knee joint
- Stiffness and
decreased or loss of range of motion
- Redness and warmth
to touch
- Popping or crepitus sounds
WHEN TO SEE THE DOCTOR ABOUT YOUR KNEE PAIN:
- Can't bear weight
on your knee or feel as if your knee is unstable or gives out
- Have marked knee
swelling
- Are unable to
fully extend or flex your knee
- See an obvious
deformity in your leg or knee
- Have a fever, in
addition to redness, pain and swelling in your knee
- Have severe knee
pain that is associated with an injury.
TREATMENT OF KNEE INJURY:
1. Medications:
The doctor may assign
medications to relieve pain, reduce inflammation and relax muscles. Rheumatoid
arthritis require special medications to be used during daily living to prevent
flare ups.
2. Physical therapy treatment:
·
PRICE therapy
(Protection, rest, icing, compression and elevation) during the initial stages
of injury.
·
Using of
modalities like hot pack, short wave diathermy, TENS, Infra-red lamps and
ultrasound to relax muscles.
·
Patellar
mobilization, knee distraction techniques and knee mobilization may be used to
mobilize the knee joint to gain range of motion and reduce pain.
·
Knee Range of
motion exercises to gain ranges if compromised.
·
Strengthening
exercises of the muscles around the knee joint, including the quadriceps,
hamstrings, tensor fascia latae, calf muscles, abductors and adductors, through
knee isometrics.
·
Stretching of
muscles that affect knee joint with their tightness.
·
Kineso-taping for
lowering load on the joint and better healing purpose, bracing can also be
considered.
3. Injections:
In some cases, your
doctor may suggest injecting medications or other substances directly into your
joint. Examples include:
·
Corticosteroids:
Injections of a corticosteroid drug into your knee joint may help reduce the
symptoms of an arthritis flare and provide pain relief that may last a few
months. These injections aren't effective in all cases.
·
Hyaluronic acid: A
thick fluid, similar to the fluid that naturally lubricates joints, hyaluronic
acid can be injected into your knee to improve mobility and ease pain. Although
study results have been mixed about the effectiveness of this treatment, relief
from one or a series of shots may last as long as six months.
·
Platelet-rich
plasma (PRP): PRP contains a concentration of many different growth factors
that appear to reduce inflammation and promote healing. Some studies have found
that PRP may benefit certain people with osteoarthritis.
4. Surgery:
Under extreme cases, when
knee injury or pain cannot be treated using conservative treatments, Surgery
may be preferred. Different types of surgeries are as follows:
- Partial knee
replacement surgery: In this procedure, the surgeon replaces only the most
damaged portion of your knee with parts made of metal and plastic. The surgery
can usually be performed through small incisions, so it mostly heals up quickly
- Total knee replacement:
In this procedure, the surgeon cuts away damaged bone and cartilage from your
thighbone, shinbone and kneecap, and replaces it with an artificial joint made
of metal alloys, high-grade plastics and polymers.
- Osteotomy: This
procedure involves removing bone from the thighbone or shinbone to better align
the knee and relieve arthritis pain. This surgery may help you delay or avoid
total knee replacement surgery.








Comments
Post a Comment